Tag Archives: filter
SP_COPYFIELDS
COPYFIELDS() Short: ------ COPYFIELDS() Copies selected fields of selected records to new dbf Returns: -------- None Syntax: ------- COPYFIELDS([aFields,[aDescript]]) Description: ------------ This metafunction allows selection of fields, and selection of record criteria (filter) to be copied to a new DBF. [aFields] is an array of valid field names. Default is all fields. Fields not of the current area are not allowed. [aDescript] is an array of field descriptions, which can only be passed if [aFields] is passed, and which must reflect the fields in [aFields] Examples: --------- use (cDbfName) COPYFIELDS() // its a metafunction... Source: ------- S_COPYF.PRG
SP_AVARIANCE
AVARIANCE()
Short:
------
AVARIANCE() Determines the variance of an array with condition
Returns:
--------
<nVariance> => Array variance
Syntax:
-------
AVARIANCE(aTarget,[bCondition])
Description:
------------
<aTarget> is the target array. Normally an array of
numeric values. [bCondition] is an optional codeblock used to
select a subset of the array. This could be used to filter out
0's or non-numeric elements. The block must accept an array
element as a parameter, and return true or false <expL> to
determine if this element is part of the desired subset.
Examples:
---------
v := AVARIANCE(aSales)
v := AVARIANCE(aSales,{|e|valtype(e)=="N".and.e<>0})
Source:
-------
S_ASTATS.PRG
SP_ASUM
ASUM()
Short:
------
ASUM() Determines the sum of an array with condition
Returns:
--------
<nArraySum> => Array sum
Syntax:
-------
ASUM(aTarget,[bCondition])
Description:
------------
<aTarget> is the target array. Normally an array of
numeric values. [bCondition] is an optional codeblock used to
select a subset of the array. This could be used to filter out
0's or non-numeric elements.
The block must accept an array element as a
parameter, and return true or false <expL> to determine if this
element is part of the desired subset.
Examples:
---------
v := ASUM(aSales)
v := ASUM(aSales,{|e|valtype(e)=="N".and.e<>0})
Source:
-------
S_ASTATS.PRG
SP_AMSUM
AMSUM()
Short:
------
AMSUM() Sum on a given element of multi-dim array
Returns:
--------
<nSum> => sum of array element
Syntax:
-------
AMSUM(aMult,nElem,[bCondition])
Description:
------------
Returns sum of array <aMult> element <nElem>.
[bCondition] is an optional codeblock used to select
a subset of the array. This could be used to filter out 0's or
non-numeric elements. The block must accept a subarray as a
parameter, and return true or false <expL> to determine if this
element is part of the desired subset. Please note that the
codeblock accepts the whole subarray, not just subarray element
<nElem>
Examples:
---------
?"Total file size here is "
??AMSUM(DIRECTORY(),2)
?"Total .EXE file size here is "
??AMSUM(DIRECTORY(),2,{|e|".EXE"$e[1]} )
use customer
?"Total field size "
??AMSUM(DBSTRUCT(),3)
use customer
?"Total CHARACTER field size "
??AMSUM(DBSTRUCT(),3,{|e|e[2]=="C"} )
Notes:
-------
Coded by Matthew Maier.
Presumes all sub-arrays are of equal length
Source:
-------
S_AMSTAT.PRG
SP_AMSTDDEV
AMSTDDEV()
Short:
------
AMSTDDEV() Standard Deviation on a given element of
multi-dim array
Returns:
--------
<nVariance> => average of array element
Syntax:
-------
AMSTDDEV(aMult,nElem,[bCondition])
Description:
------------
Returns Standard Deviation of array <aMult> element
<nElem>. [bCondition] is an optional codeblock used to select a
subset of the array. This could be used to filter out 0's or
non-numeric elements.
The block must accept a subarray as a parameter, and
return true or false <expL> to determine if this element is
part of the desired subset. Please note that the codeblock
accepts the whole subarray, not just subarray element <nElem>
Examples:
---------
?"Total file size here is "
??AMSUM(DIRECTORY(),2)
?"Total .EXE file size here is "
??AMSUM(DIRECTORY(),2,{|e|".EXE"$e[1]} )
?"Standard Deviation:"
??AMSTDDEV(DIRECTORY(),2,{|e|".EXE"$e[1]} )
Notes:
-------
Coded by Matthew Maier.
Presumes all sub-arrays are of equal length
Source:
-------
S_AMSTAT.PRG
SP_AMAVERAGE
AMAVERAGE()
Short:
------
AMAVERAGE() Average on a given element of multi-dim array
Returns:
--------
<nAverage> => average of array element
Syntax:
-------
AMAVERAGE(aMult,nElem,[bCondition])
Description:
------------
Returns average of array <aMult> element <nElem>.
[bCondition] is an optional codeblock used to select
a subset of the array. This could be used to filter out 0's or
non-numeric elements. The block must accept a subarray as a
parameter, and return true or false <expL> to determine if this
element is part of the desired subset.
Please not that the codeblock accepts the whole
subarray, not just subarray element <nElem>
Examples:
---------
?"Average file size here is "
??amaverage(DIRECTORY(),2)
?"Average .EXE file size here is "
??amaverage(DIRECTORY(),2,{|e|".EXE"$e[1]} )
use customer
?"Average field size "
??amaverage(DBSTRUCT(),3)
Notes:
-------
Presumes all sub-arrays are of equal length
Coded by Matthew Maier.
Source:
-------
S_AMSTAT.PRG
SP_AAVERAGE
AAVERAGE()
Short:
------
AAVERAGE() Determines average of an array with condition
Returns:
--------
<nAverage> => Average of the array
Syntax:
-------
AAVERAGE(aTarget,[bCondition])
Description:
------------
<aTarget> is the target array. Normally an array of numeric values.
[bCondition] is an optional codeblock used to select
a subset of the array. This could be used to filter out 0's or
non-numeric elements. The block must accept an array element as
a parameter, and return true or false <expL> to determine if
this element is part of the desired subset.
Examples:
---------
v := AAVERAGE(aSales)
v := AAVERAGE(aSales,{|e|valtype(e)=="N".and.e<>0})
Source:
-------
S_ASTATS.PRG
HbRun
HbRun is a console interpreter and program ( command file / script file / .prg / .hrb ) runner for the Harbour Language.
Addendum: a clarification by Przemek:
HBRUN is a simple wrapper to Harbour compiler so the same syntax as in
Cl*pper is supported:
DO <filename>[.prg]
only .prg is accepted as extension and it’s default so you do not
have to set it explicitly.
( In Harbour Users Google group, under “hbmk2 and the Dot Prompt” topic:
It can work as interpreter when invoked without parameters or can execute xBase / Harbour source code in .prg file or compiled Harbour Portable Objects (.hrb) file given as parameter.
Type of file is recognized by extension used with <file> parameter. If not given then .hrb is used.
In other words, HbRun can be use in both interpret and batch mode.
Regarding parameter given or not, when calling HbRun this ‘mode’ determined by program itself. If a parameter ( usually a .prg or .hrb file name ) given, program run in ‘batch’ mode, runs (executes) given script file and end. If no parameter given, program enter interpreter mode.
Using HbRun as an interpreter, may be very useful, productive, and educative for xBase programmers. Too many xBase programmers was learned everything, including DBF file system and xBase programming language by famous “dot prompt”. Today many xBase programmers uses HbRun daily basis.
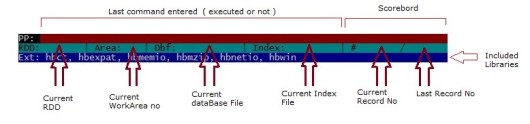
When HbRun begin, open a console screen with two basic area: status bars at top and dot prompt line at bottom.
Status bars :
Dot prompt is quite simple visually: a dot and a line in inverse color beginning with a blinking cursor :
You may enter here a command to see the result.
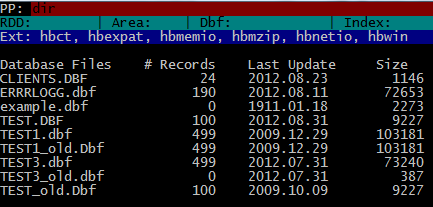
For example “DIR” command will give a list of database (.dbf) files in current directory:
SET COLO TO “GR+/N” command will remember you old days :
The DIR command can be used with DOS style “filter / skeleton” parameter :
DIR *.PRG
DIR *.*
etc.
Inspecting any table ( .dbf file ) is very simple:
USE CLIENTS
BROWSE ()
Expand a little:
SET COLO TO “GB+/N”
USE CLIENTS
BROWSE( 3, 10, 24, 60 )
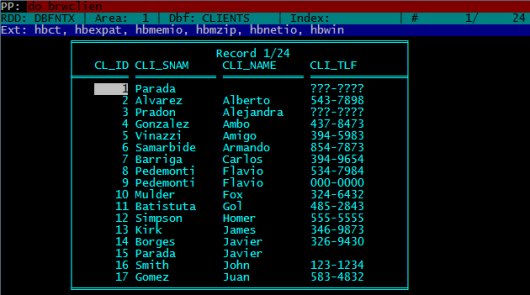
If you plan to use this snap frequently, make a .prg file (say brwclien.prg) with this three line and run it with DO command:
DO BRWCLIEN
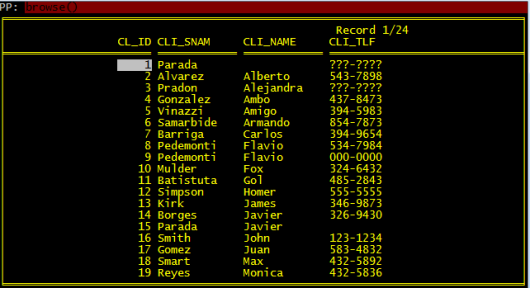
Sometime LIST command may be better:
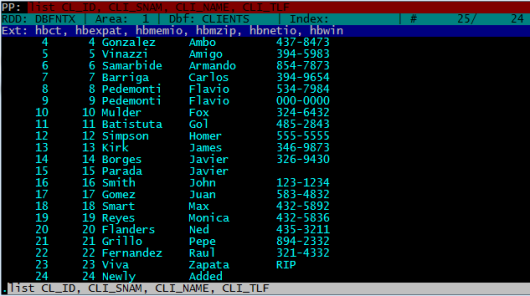
LIST CL_ID, CLI_SNAM, CLI_NAME, CLI_TLF
You can add FOR clause to the LIST command:
LIST CL_ID, CLI_SNAM, CLI_NAME, CLI_TLF FOR RECN() < 10
or
LIST CL_ID, CLI_SNAM, CLI_NAME, CLI_TLF FOR EMPTY( CLI_TLF )
The structure info of a table frequently requires while daily work to xBase Programmers.
Here three small programs for obtain structure info of a table. Usage is quite simple: open ( USE ) your table and enter DO <prgFileName>; for example:
USE CLIENT
DO LISTSTRU
or
DO DISPSTRU
or
DO SAVESTRU
Notes :
– To avoid some possible screen metric conflicts caused by default console (DOS box) settings of OS, may be useful some adjusting before invoke HbRun; such as:
MODE CON LINES=48 COLS=128
– “?” command may be useful as a built-in calculator :
? 2*2 // 4
? 2**8 // 256
? SQRT( 81 ) // 9
– HbRun keep a “history” for commands entered (for a limited count of commands of course). You can access (and re-enter when required) by using up and down keys. Moreover this history may be usable after re-invoke HbRun.
– Though Harbour Language is essential, some legal Harbour commands / functions may be un-recognizable by HbRun.
– Though some legal statements works in interpret mode, may not works in batch mode (such as Browse() ).
Last Note : No further explanation required for experienced xBase programmers; try, see and learn.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Examples :
/*
DispStru.prg
Display structure of current table ( .dbf file ) on screen.
*/
MEMVAR ASTRUCT, NTOTLEN
IF EMPTY( ALIAS() )
SETCOLOR( "R/N" )
? "No active table in the current work area !", LTRIM( STR( SELECT() ) )
ELSE
@ 3, 0 CLEA TO MAXROW() - 1, MAXCOL()
aStruct := DBSTRUCT()
nTotLen := 1
AEVAL( aStruct, { | a1Field | nTotLen += a1Field[ 3 ] } )
AEVAL( aStruct, { | a1Field, n1FieldNo | ;
aStruct[ n1FieldNo ] := STR( n1FieldNo, 3 ) + " " +;
PADR( a1Field[ 1 ], 12 ) +;
PADC( a1Field[ 2 ], 4 ) +;
PADL( a1Field[ 3 ], 5 ) +;
PADL( a1Field[ 4 ], 3 ) } )
? "Structure of database :", DBINFO( 10 )
? "Number of data records :", LTRIM( STR( LASTREC() ) )
? "Date of last update :", LUPDATE()
? "Fld Name Type Width Dec"
? "--- ---------- ---- ----- ---"
@ 21,0 SAY "** Total ** " + PADL( nTotLen, 6 )
ACHOICE( 8, 0, 20, 30, aStruct )
ENDIF
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
/*
ListStru.prg
List structure of current table ( .dbf file ) on screen.
*/
MEMVAR ASTRUCT, NTOTLEN
IF EMPTY( ALIAS() )
SETCOLOR( "R/N" )
? "No active table in the current work area !", LTRIM( STR( SELECT() ) )
ELSE
@ 3, 0 CLEA TO MAXROW() - 1, MAXCOL()
aStruct := DBSTRUCT()
nTotLen := 1
AEVAL( aStruct, { | a1Field | nTotLen += a1Field[ 3 ] } )
AEVAL( aStruct, { | a1Field, n1FieldNo | ;
aStruct[ n1FieldNo ] := STR( n1FieldNo, 3 ) + " " +;
PADR( a1Field[ 1 ], 12 ) +;
PADC( a1Field[ 2 ], 4 ) +;
PADL( a1Field[ 3 ], 5 ) +;
PADL( a1Field[ 4 ], 3 ) } )
? "Structure of database :", DBINFO( 10 )
? "Number of data records :", LTRIM( STR( LASTREC() ) )
? "Date of last update :", LUPDATE()
? "Fld Name Type Width Dec"
? "--- ---------- ---- ----- ---"
AEVAL( aStruct, { | c1Field | QOUT( c1Field ) } )
? "** Total ** ", PADL( nTotLen, 5 )
ENDIF
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
/*
SaveStru.prg
Save structure of current table ( .dbf file ) to a file.
Notes :
- This program uses ListStru.prg
- Name of target file constructed at line 18;
if required you may use alternate ways or
simply using a constant.
*/
MEMVAR AlteFName
IF EMPTY( ALIAS() )
SETCOLOR( "R/N" )
? "No active table in the current work area !", LTRIM( STR( SELECT() ) )
ELSE
AlteFName := LEFT( ALIAS(), 4 ) + "STRU"
SET ALTE TO &AlteFName
SET ALTE ON
DO LISTSTRU
SET ALTE OFF
SET ALTE TO
ENDIF
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~